The Basics of Currency Pairs: A Comprehensive Guide
11/07/2024
How to Read Forex Charts: A Comprehensive Guide
11/07/2024Understanding Forex Quotes: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Forex Quotes
In the world of Forex trading, understanding how currency quotes work is fundamental to making informed trading decisions. Forex quotes represent the price of one currency in terms of another currency, and they are the basis for all currency trading transactions. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of Forex quotes, covering how they are structured, what influences them, and how traders can use this information to their advantage. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to deepen your knowledge, this article will provide valuable insights into the complex world of Forex quotes.

What is a Forex Quote?
A Forex quote displays the value of one currency in terms of another currency. It is composed of two currencies, known as a currency pair, and it shows how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. For example, in the EUR/USD pair, the euro (EUR) is the base currency, and the US dollar (USD) is the quote currency. A quote of 1.2000 means that one euro is worth 1.2000 US dollars.
Structure of a Forex Quote
A typical Forex quote includes the following components:
Currency Pair
Currency pairs are presented in a specific format, consisting of the base currency and the quote currency. The base currency is listed first, followed by the quote currency. Some common currency pairs include:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar)
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar)
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen)
- USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc)
Bid and Ask Price
A Forex quote always includes two prices: the bid price and the ask price. The bid price is the price at which the market (or your broker) is willing to buy the base currency in exchange for the quote currency. The ask price, also known as the offer price, is the price at which the market (or your broker) is willing to sell the base currency in exchange for the quote currency. The difference between the bid and ask prices is known as the spread.
Example of a Forex Quote
Consider the EUR/USD currency pair quoted as 1.2000/1.2003. Here, 1.2000 is the bid price, and 1.2003 is the ask price. If you want to buy euros, you would pay the ask price of 1.2003. If you want to sell euros, you would receive the bid price of 1.2000. The spread in this example is 0.0003, or 3 pips.
Understanding Pips and Pipettes
What is a Pip?
A pip (percentage in point) is the smallest price movement in a currency pair. For most currency pairs, a pip is equal to 0.0001. For currency pairs involving the Japanese yen, a pip is equal to 0.01. Pips are used to measure price movements and calculate profits or losses in Forex trading.
What is a Pipette?
Some brokers quote currency pairs with an additional decimal place, known as a pipette. This allows for more precise pricing. For example, instead of quoting EUR/USD as 1.2000, a broker might quote it as 1.20005. In this case, the fifth decimal place represents a pipette, or one-tenth of a pip.
Direct and Indirect Quotes
Forex quotes can be classified into two types: direct quotes and indirect quotes.
Direct Quote
A direct quote expresses the amount of domestic currency needed to buy one unit of foreign currency. For example, if you are in the United States and looking at the EUR/USD pair, a quote of 1.2000 means that it costs 1.2000 US dollars to buy one euro. In this scenario, the direct quote is USD/EUR = 0.8333, which means one US dollar is worth 0.8333 euros.
Indirect Quote
An indirect quote expresses the amount of foreign currency needed to buy one unit of domestic currency. Using the same example, if the EUR/USD pair is quoted at 1.2000, the indirect quote would be EUR/USD = 1.2000, meaning one euro is worth 1.2000 US dollars.
Base Currency and Quote Currency
Base Currency
The base currency is the first currency listed in a currency pair. It is the currency you are buying or selling when you trade the pair. For example, in the EUR/USD pair, the euro is the base currency. If you buy the EUR/USD pair, you are buying euros and selling US dollars.
Quote Currency
The quote currency is the second currency listed in a currency pair. It is the currency you are using to buy or sell the base currency. In the EUR/USD pair, the US dollar is the quote currency. If you buy the EUR/USD pair, you are using US dollars to buy euros.
Major, Minor, and Exotic Currency Pairs
Major Currency Pairs
Major currency pairs consist of the world’s most traded currencies and include the US dollar. They typically have high liquidity and low spreads. Examples of major pairs are:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar)
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar)
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen)
- USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc)
Minor Currency Pairs
Minor currency pairs, also known as cross-currency pairs, do not include the US dollar but involve other major currencies. They usually have lower liquidity and higher spreads compared to major pairs. Examples of minor pairs are:
- EUR/GBP (Euro/British Pound)
- EUR/AUD (Euro/Australian Dollar)
- GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen)
- CHF/JPY (Swiss Franc/Japanese Yen)
Exotic Currency Pairs
Exotic currency pairs consist of one major currency and one currency from an emerging or smaller economy. They generally have lower liquidity and higher spreads, making them more volatile and riskier to trade. Examples of exotic pairs include:
- USD/TRY (US Dollar/Turkish Lira)
- EUR/SEK (Euro/Swedish Krona)
- GBP/ZAR (British Pound/South African Rand)
- USD/HKD (US Dollar/Hong Kong Dollar)
Factors Influencing Forex Quotes
Several factors influence the price movements of Forex quotes. Understanding these factors can help traders make informed decisions and develop effective trading strategies.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators are statistics that reflect the economic performance of a country. Key indicators include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Measures the total value of goods and services produced by a country. A strong GDP growth rate typically strengthens a country’s currency.
- Inflation: Measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI) or Producer Price Index (PPI). Higher inflation can lead to higher interest rates, which can strengthen a currency.
- Employment Data: Indicators such as the Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) report provide insights into the health of the labor market. High employment rates usually strengthen a currency.
- Interest Rates: Central bank interest rate decisions have a significant impact on currency values. Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency.
Political Events
Political stability and events, such as elections, government policies, and geopolitical tensions, can cause significant volatility in the Forex market. Traders closely monitor political developments to anticipate potential market movements.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment reflects the overall attitude of investors toward a particular currency pair. Sentiment can be influenced by economic data, news events, and market rumors. Positive sentiment generally strengthens a currency, while negative sentiment weakens it.
Central Bank Policies
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve, the European Central Bank, and the Bank of Japan, play a crucial role in the Forex market. Their monetary policies, including interest rate decisions and quantitative easing programs, directly impact currency values.
Trade Balances
A country’s trade balance, which is the difference between its exports and imports, can influence its currency. A positive trade balance (surplus) indicates more exports than imports, which can strengthen the currency. Conversely, a negative trade balance (deficit) can weaken the currency.
How to Read Forex Quotes
Reading Forex quotes can initially seem confusing, but it becomes straightforward once you understand the components. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to read Forex quotes:
Identify the Currency Pair
The first step is to identify the currency pair being quoted. Remember that the first currency is the base currency, and the second is the quote currency.
Understand the Bid and Ask Prices
The quote will display two prices: the bid and the ask. The bid price is where the market will buy the base currency, and the ask price is where the market will sell the base currency.
Calculate the Spread
The spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices. It represents the cost of the trade and the broker’s profit margin. Lower spreads are generally better for traders as they reduce trading costs.
Example of Reading a Forex Quote
Consider the EUR/USD quote: 1.2000/1.2003. Here’s how to read it:
- Currency Pair: EUR/USD
- Bid Price: 1.2000 (you sell EUR to buy USD)
- Ask Price: 1.2003 (you buy EUR with USD)
- Spread: 0.0003 (3 pips)
Using Forex Quotes in Trading
Forex quotes are essential for making trading decisions. Here are some strategies for using Forex quotes effectively in your trading:
Analyzing Trends
Traders analyze historical Forex quotes to identify trends. By examining price movements over time, traders can determine whether a currency pair
is in an uptrend, downtrend, or sideways trend. Trend analysis helps traders make informed decisions about when to enter or exit trades.
Setting Entry and Exit Points
Forex quotes help traders set entry and exit points for their trades. By understanding the bid and ask prices, traders can determine the best price levels to buy or sell a currency pair. Technical analysis tools, such as support and resistance levels, can further refine these entry and exit points.
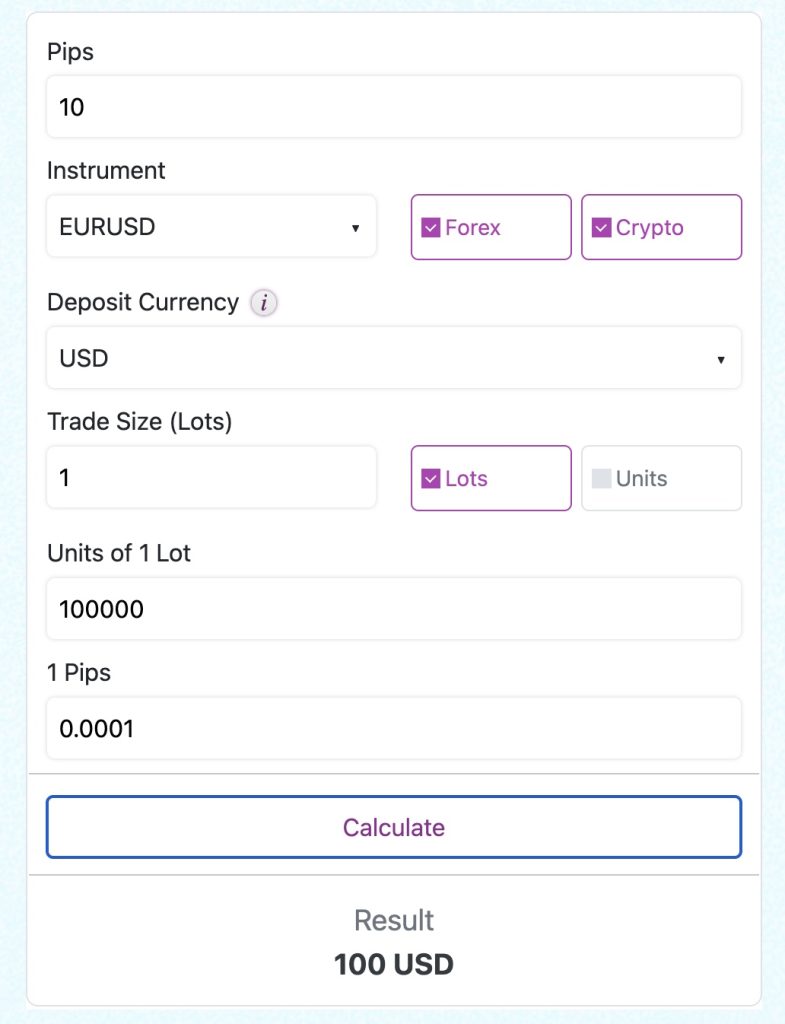
Calculating Profit and Loss
Traders use Forex quotes to calculate potential profit and loss for their trades. By comparing the entry price to the exit price, traders can determine how many pips they gained or lost. Knowing the value of each pip for the specific currency pair helps in calculating the exact profit or loss in monetary terms.
Implementing Risk Management
Risk management is crucial in Forex trading. Traders use Forex quotes to set stop-loss and take-profit orders, which automatically close their positions at predefined price levels. This helps limit potential losses and secure profits.
Common Mistakes When Interpreting Forex Quotes
Ignoring the Spread
One common mistake is ignoring the spread when interpreting Forex quotes. The spread affects the overall cost of the trade and can impact profitability, especially for short-term trades. Always consider the spread when planning your trades.
Overlooking Market Volatility
Forex quotes can change rapidly due to market volatility. Traders who overlook this volatility may enter trades at unfavorable prices or experience slippage. It’s essential to stay updated with market news and be aware of potential volatility.
Misinterpreting Bid and Ask Prices
Some traders misinterpret the bid and ask prices, leading to incorrect trading decisions. Remember that the bid price is for selling the base currency, and the ask price is for buying the base currency. Ensure you understand these terms before placing trades.
Ignoring Economic Indicators
Economic indicators significantly impact Forex quotes. Ignoring these indicators can result in poor trading decisions. Stay informed about key economic releases and how they might affect currency values.
Conclusion
Understanding Forex quotes is fundamental to successful trading in the Forex market. By grasping the structure of currency pairs, the significance of bid and ask prices, and the factors influencing currency movements, traders can make more informed and strategic decisions. Implementing effective risk management practices and staying updated with market news further enhances trading success. With this comprehensive guide, you are now equipped with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of Forex quotes and improve your trading performance.
-
Understanding Forex Quotes: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Forex Quotes: A Comprehensive Guide Introduction to Forex Quotes In the world of Forex trading, understanding how currency quotes work is fundamental to making informed […]